A recent extensive study reveals that women who adhere closely to a Mediterranean diet tend to live significantly longer than those who do not. This research, which tracked over 25,000 women for a quarter of a century, highlights the potential benefits of this dietary pattern.
According to Dr. Samia Mora, a cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, “For women aiming for longevity, our study indicates that following a Mediterranean diet could lead to a roughly 25% reduction in the risk of death over more than 25 years, benefiting both cancer and cardiovascular mortality—the leading causes of death.”
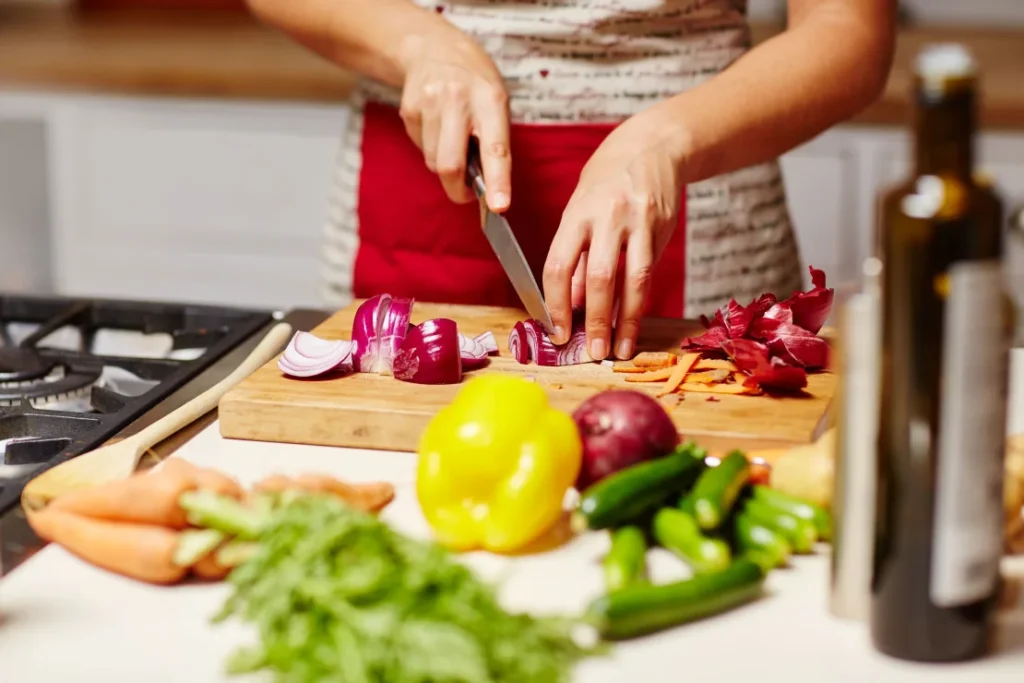

The Mediterranean diet emphasizes simple, plant-based cooking with a focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, and seeds. It includes some nuts and a significant amount of extra-virgin olive oil while minimizing the intake of other fats like butter, as well as sugar and refined foods. Red meat is used sparingly, primarily to flavor dishes, and there is an encouragement to consume healthy, oily fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Eggs, dairy, and poultry are eaten in smaller quantities compared to a traditional Western diet.
Dr. David Katz, a preventive and lifestyle medicine expert and founder of the nonprofit True Health Initiative, noted that adherence to the Mediterranean diet is an indicator of overall diet quality. He mentioned that those who followed the diet closely consumed more legumes, vegetables, and fruits, while eating less meat and fewer processed meats. Although the study is observational and cannot establish a direct cause-and-effect relationship, Katz pointed out that its findings align with numerous other studies on the health benefits of the Mediterranean diet. “We can reasonably infer that a high-quality diet did, indeed, lower the risk of death,” Katz stated.
The study also found that each increase in adherence to the Mediterranean diet extended life expectancy for women.
Importance of Studying Women
The Mediterranean diet is known for its numerous health benefits, such as reducing the risk of breast cancer, dementia, depression, diabetes, high cholesterol, and memory loss. It also contributes to stronger bones, a healthier heart, longer life, and healthy weight loss. However, specific details on how the diet affects women long-term have been scarce. This is crucial because women have unique physiological differences compared to men, including different heart sizes, brain functions, symptoms of heart attacks, and responses to alcohol and medications.
Key Findings of the Study
Published in JAMA Network Open, the study involved 25,315 healthy women from the Women’s Health Study. Researchers collected dietary data and biomarkers between 1993 and 1996, with follow-ups from 2018 to 2023. The findings showed that strict adherence to the Mediterranean diet reduced the risk of early death by 23%, cancer mortality by 17%, and cardiovascular mortality by 20%. Lead author Shafqat Ahmad, an associate professor at Uppsala University, highlighted that greater adherence to the diet was associated with a 6% lower risk of all-cause mortality and a 5% reduced risk of dying from heart disease or cancer.
Dr. Katz emphasized the study’s methodology, which corrected for potential distortions of the Mediterranean diet, ensuring the results reflected adherence to a genuine Mediterranean dietary pattern.
Tips for Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
Experts suggest incorporating more vegetables and legumes into meals, using a variety of colors and types to maximize nutrient intake. Cooking with extra-virgin olive oil, adding whole grains and fruits to every meal, and using nuts and seeds sparingly due to their high-calorie content are recommended. Red meat consumption should be minimized, with a preference for fish and seafood, which should be eaten at least twice a week. Protein sources should primarily come from beans and other legumes. Cheese and yogurt can be consumed in moderation, while chicken, pork, and eggs are suitable occasionally. Sweets should be reserved for special occasions, with fresh and frozen fruit as healthier alternatives.
By adopting these dietary habits, individuals can enjoy the myriad health benefits associated with the Mediterranean diet.